| Home > Reviews > The Deltapod: A New Parallel Robot for Flexible Fixturing Applications | |
The Deltapod: A New Parallel Robot for Flexible Fixturing Applications |
|
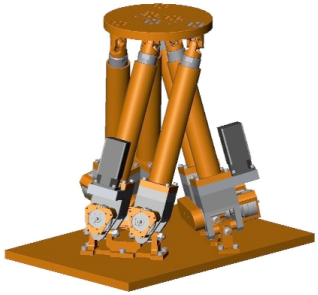
IntroductionABB has just launched a new type of parallel kinematic machine (PKM), dubbed the FlexPLP (Flexible Principle Locator Points), designed for flexible fixturing tasks. The FlexPLP is intended to replace fixed locator points – which are used to define the geometry of car body parts during framing and welding – with numerically controlled locator points. A parallel kinematic machine called Deltapod was developed to freely position the locator pins in space.
The DeltapodThe Deltapod represents a combination of well-known Delta and hexapod principles. It consists of three pairs of parallelly arranged electrical cylinders, forming the legs of the machine. By arranging the leg pairs in tilted fashion, foot print of the machine could be minimized, while keeping the other key machine parameters constant. The result is a very compact but powerful machine that can carry payloads exceeding four times its own mass. The first application of the new machine is part fixturing in a flexible automotive bodyshop. Four or more FlexPLPs are arranged on a linear track, fixturing car underbodies and serving welding stations as flexible shuttles, adapting to each car model. The shuttles pick up unfinished car bodies form one station and transport them to the next station where they are received by stationary Cartesian flexible positioners. This new principle, part of ABB's FlexLean concept, allows to eliminate the large number of fixed pallets used for transport of car bodies through the factory today, and allows for multi-model production. Since this application requires only three degrees of freedom for each machine, a hexapod with six motors would not reach the cost target. Therefore, ABB invented and patented a mechanical coupling between the cylinders, which allows to drive a pair of cylinders with a single motor. One Deltapod requires only three motors, just like a Delta robot. This reduces the cost on the amplifier and controller side — ABB's robot controller IRC5 is able to control twelve of these three-axis machines.
Related Links
|
|
Home |
Bibliography |
Patents |
Terminology |
Reviews |
Software |
Who's Who |
News Site Map | Site Search | Contact Us | About Us |
| Copyright © 2000– by Ilian Bonev | Published on: November 16, 2007 |